Understanding how valves car engine systems work makes a significant difference in vehicle maintenance and performance. These critical components control the precise flow of air and fuel into the engine, while managing the exit of exhaust gases.
Though often overlooked during routine maintenance, valves stand as the gatekeepers of engine efficiency and power output. Their condition and operation affect every aspect of how an engine performs.
The Basics of Engine Valve Operation
Car engine valves work in perfect coordination with multiple components to control the four-stroke cycle. Each cylinder needs both intake and exhaust valves for proper operation. The precise timing of these valves opening and closing directly influences engine performance, fuel economy, and emissions.
Modern automotive technology continues pushing valve designs forward, creating more efficient and powerful engines through better breathing characteristics.
Types of Valves in Modern Engines
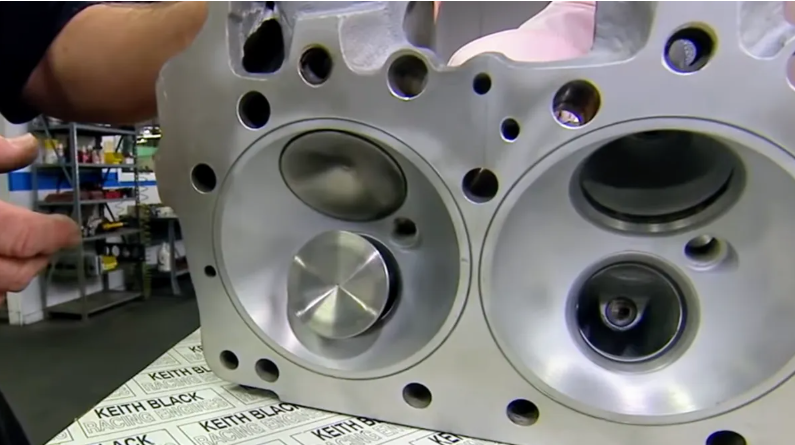
Modern engines employ various valve configurations based on their design and intended purpose. A valve car engine might feature anywhere from two to four valves per cylinder, each chosen to meet specific performance goals.
High-performance engines typically use multiple valves to improve airflow and power output. These configurations vary based on manufacturer specifications and intended use, with each design offering unique advantages.
How Valves Affect Engine Performance
The design and condition of valves in car engine systems play a decisive role in overall performance. Well-maintained valves ensure proper compression, efficient fuel burning, and optimal power delivery.
Poor valve condition leads to reduced performance and increased fuel consumption. The relationship between valve operation and engine performance becomes even more pronounced at higher RPMs.
Common Valve Configurations
- Basic Two-Valve Design
- One intake valve and one exhaust valve represent the traditional approach
- Simple and reliable design provides good performance for many applications
- Lower maintenance requirements suit daily driving needs
- Common in many proven engine designs
- Cost-effective for manufacturing and repairs
- Multi-Valve Systems
- Multiple intake and exhaust valves improve engine breathing
- Enhanced performance through better airflow management
- More complex design requires careful maintenance
- Modern engineering focuses on reliability
- Advanced materials improve longevity
Maintenance and Care
Regular maintenance prevents most valve-related problems before they start. Professional mechanics emphasize the value of periodic valve adjustments and inspections to maintain proper clearances and prevent excessive wear. These routine checks often reveal developing issues before they become serious problems, saving both time and money in the long run.
Signs of Valve Problems
Recognizing potential valve issues early prevents serious engine damage. Problems typically begin with subtle changes in engine operation that worsen over time. Rough idle conditions, noticeable power loss, and unusual noises indicate possible valve concerns.
Regular maintenance catches these issues before major repairs become necessary, preserving both performance and reliability.
Performance Modifications
Many car enthusiasts modify their valves car engine components to increase performance. These changes might include larger valves, different valve materials, or altered timing specifications. Careful planning ensures modifications work together effectively.
Popular Upgrades
Performance upgrades often focus on improving airflow through the engine. Better flowing valves and ports help engines produce more power, especially at higher RPMs. Proper component matching ensures reliable operation under increased stress.
The Role of Valve Timing
Proper valve timing ensures optimal engine operation. Modern engines often use variable valve timing to balance performance and efficiency across different operating conditions. This technology adapts to changing driving demands automatically.
Variable Timing Systems
Variable timing systems adjust valve operation based on engine speed and load. This technology helps engines deliver both good low-end torque and high-end power. Advanced control systems fine-tune operation for best results.
Materials and Construction
Different valve materials suit different applications. Standard car engine valves typically use durable but affordable materials, while performance applications might use more exotic options. Material selection balances cost, durability, and performance requirements.
Material Selection Factors
Valve materials must withstand extreme temperatures and pressures while maintaining proper sealing. Operating temperatures, budget constraints, and performance goals influence material choices. Regular inspection ensures materials perform as intended.
Heat Management
Valves handle extreme temperatures, especially exhaust valves. Proper cooling and material selection help prevent heat-related failures. Modern designs incorporate various cooling strategies for reliable operation.
Cooling Considerations
Modern engines use several methods to manage valve temperatures. Sodium-filled valves help transfer heat away from valve faces. Improved coolant flow patterns enhance overall cooling efficiency. Better metallurgy provides increased heat resistance.
Performance Testing
Measuring valve performance helps optimize engine operation. Various testing procedures provide data about valve movement, sealing, and flow characteristics. Regular testing ensures continued proper operation.
Racing Applications
Racing pushes valve car engine systems to their limits. Competition engines often use specialized valve components to handle increased stress and heat. Track use requires careful attention to maintenance schedules.
Daily Driving Considerations
Street-driven vehicles need reliable valve operation across various conditions. Proper maintenance helps ensure consistent performance and longevity. Regular service prevents unexpected problems.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Understanding common valve problems helps diagnose issues quickly. Early detection prevents minor problems from becoming major repairs. Professional inspection provides accurate diagnosis.
Modern Technology
New technologies continue improving valves in car engine performance. Innovations in materials and design create more efficient and reliable valve systems. Electronic controls offer precise operation.
Environmental Impact
Valve design affects engine emissions and efficiency. Modern engines use sophisticated valve control to reduce emissions while maintaining performance. Proper maintenance ensures clean operation.
Cost Considerations
Valve maintenance and repairs vary in cost depending on the engine design and required work. Prevention often costs less than fixing major problems. Quality parts provide better value over time.
Future Trends
Engine technology continues evolving, with new approaches to valve control and operation. These developments promise better performance and efficiency. Innovation drives constant improvement.
Conclusion
Understanding valves in car engine systems provides the foundation for better performance and reliability. Whether maintaining a daily driver or building a performance engine, proper valve care ensures optimal operation through every driving condition.
Regular maintenance, quality replacement parts, and attention to potential problems help prevent expensive repairs while maintaining engine efficiency and power.
The evolution of valve technology continues bringing improvements in both performance and reliability, making modern engines more capable than ever before.