A manhole is an essential feature of urban infrastructure, providing access to underground utilities such as sewer systems, electrical lines, and drainage networks. These openings are crucial for maintenance, repairs, and inspections, ensuring the smooth operation of various underground facilities.
What Is a Manhole?
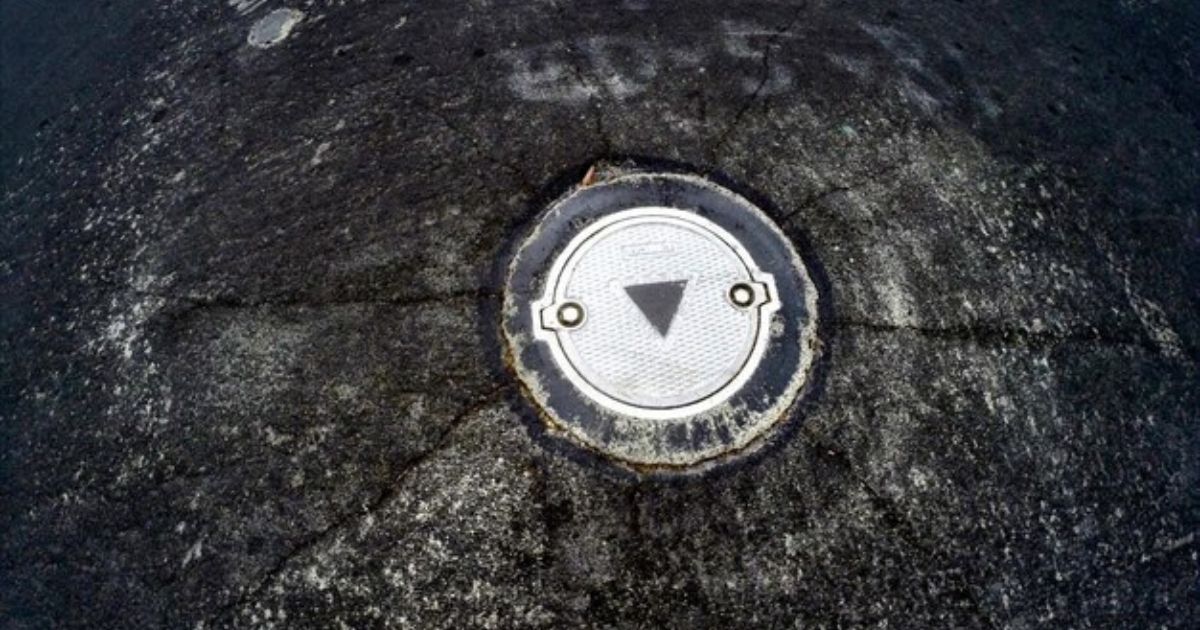
A manhole is a vertical access point that connects the surface to underground utilities. It is typically covered by a manhole cover, a heavy lid made of cast iron, concrete, or composite materials, designed to prevent unauthorized access and ensure safety.
Purpose of a Manhole
Manholes serve multiple functions in city planning and infrastructure, including:
Access to Underground Utilities: Workers use manholes to enter sewer systems, electrical vaults, and cable networks for repairs and maintenance.
Ventilation for Sewer Lines: They allow gases to escape from underground sewer lines, reducing pressure buildup.
Drainage Inspection and Cleaning: Regular checks help prevent blockages and ensure smooth wastewater flow.
Connectivity for Utility Networks: They serve as junction points for underground pipes, cables, and drainage systems.
Types of Manholes
Manholes come in different sizes and structures based on their function and location. The primary types include:
Shallow Manholes
These are small manholes, usually 600 mm to 900 mm deep, used in areas with less traffic. They provide access for minor maintenance tasks.
Normal Manholes
These standard-sized manholes, ranging from 1.2 to 1.5 meters deep, are commonly found on streets and sidewalks. They allow workers to perform regular inspections and repairs.
Deep Manholes
These structures are deeper than 1.5 meters, often requiring a ladder or steps for access. They are placed in areas with extensive underground networks and high traffic.
Manhole Cover Design and Materials
Manhole covers protect underground utilities while allowing authorized personnel to access them. The materials used include:
Cast Iron: Durable and resistant to heavy loads, commonly used in high-traffic areas.
Concrete: Used in low-traffic areas where weight is not a concern.
Composite Materials: Lightweight and resistant to theft, often found in modern city designs.
Safety Concerns with Manholes
While manholes are essential, they also pose certain risks, including:
Falls and Injuries: Open or damaged manholes can cause accidents for pedestrians and vehicles.
Gas Accumulation: Harmful gases, such as methane and hydrogen sulfide, can build up inside sewer manholes, making them dangerous for workers.
Flooding Hazards: Inadequate drainage maintenance can lead to overflowing manholes during heavy rains.
Manhole Inspection and Maintenance
To ensure the proper functioning of underground utilities, regular inspection and maintenance of manholes are necessary. This involves:
Checking for Structural Damage: Cracks or collapses in manholes can cause road hazards andservice disruptions.
Clearing Blockages: Removing debris, sediment, and waste buildup ensures smooth water and sewage flow.
Gas Detection and Ventilation: Workers test for toxic gases before entering a manhole for safety.
Theft and Vandalism of Manhole Covers
In some regions, manhole covers are stolen for their metal value, leading to safety risks and financial losses. Cities are now using composite or locking covers to prevent theft and unauthorized access.
Modern Innovations in Manhole Design
Recent advancements have improved the functionality and safety of manholes, including:
Smart Manholes: Equipped with sensors to monitor gas levels, temperature, and water flow.
Locking Mechanisms: Prevent unauthorized entry and theft.
Lightweight Materials: Reduce weight while maintaining durability, making them easier to handle.
Conclusion
Manholes are crucial for urban infrastructure, requiring proper design, maintenance, and safety measures to function efficiently and prevent hazards. Innovations in technology enhance their durability and security.
FAQs
Why are manhole covers round?
Manhole covers are round because they cannot fall into the hole, ensuring safety and ease of handling.
How often should manholes be inspected?
Manholes should be inspected every few months, depending on usage and location, to prevent blockages and damage.
What are smart manholes?
Smart manholes use sensors to detect gas levels, water flow, and temperature changes, improving maintenance efficiency.
How are manhole covers made theft-resistant?
Some cities use composite materials, locking covers, and GPS tracking to prevent theft.
Can manholes cause accidents?
Yes, open or broken manholes can cause falls, injuries, and vehicle damage, highlighting the need for regular maintenance.