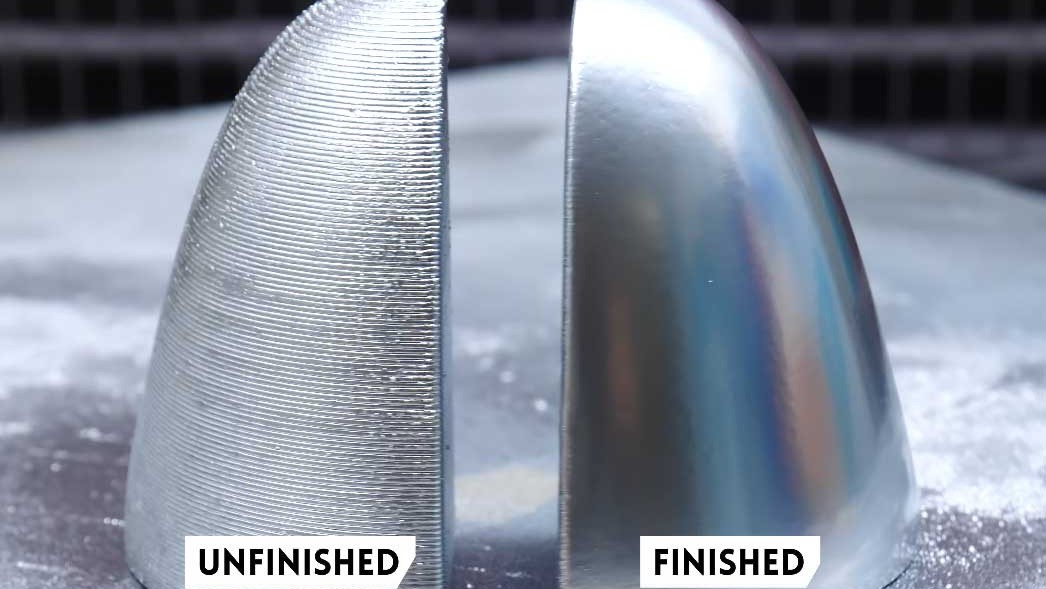
The finishing surface plays a crucial role in various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and interior design. It refers to the final treatment applied to a material to enhance its appearance, durability, and functionality. Whether in woodworking, metal fabrication, or concrete finishing, achieving a high-quality finishing surface is essential for both aesthetic appeal and long-term performance.
In this article, we will explore the significance of finishing surface, the different types, their applications, and key factors to consider when selecting the right finish.
What is a Finishing Surface?
A finishing surface is the outermost layer of a material that undergoes a treatment process to improve its properties. It can involve polishing, coating, painting, or chemical treatments to achieve a smooth, protective, and visually appealing finish. The purpose of a finishing surface varies depending on the application, but it generally serves to:
- Protect the material from corrosion, wear, or environmental damage.
- Enhance the visual appeal by adding shine, texture, or color.
- Improve functionality, such as increasing friction for better grip or making surfaces water-resistant.
Types of Finishing Surfaces
Different industries require various types of finishing surfaces, each with its unique characteristics and benefits. Below are some of the most common types:
- Mechanical Finishing
Mechanical finishing involves physical processes such as grinding, buffing, and polishing to create a smooth and refined finishing surface. This method is widely used in metalworking, where materials like stainless steel and aluminum require a polished look.
- Chemical Finishing
This type of finishing uses chemical treatments to alter the surface properties of a material. Examples include anodizing, which enhances the durability of aluminum, and acid etching, which creates textured surfaces on metals and glass.
- Coating Finishing
Coatings such as paint, powder coating, and electroplating are applied to create a protective and decorative finishing surface. These coatings protect materials from moisture, UV exposure, and corrosion while improving their appearance.
- Thermal Finishing
In thermal finishing, heat is used to modify the finishing surface. This includes heat treatments like carburizing, which strengthens metal surfaces, and flame polishing, which enhances the clarity of acrylic and plastic materials.
- Textured Finishing
Textured finishes are designed to add grip, reduce glare, or create decorative effects. Sandblasting, embossing, and brushed metal finishes are common examples of textured finishing surfaces used in construction and industrial design.
- Natural Finishing
Some materials, such as wood and stone, are left with a natural finishing surface to preserve their organic beauty. Treatments like oiling and waxing help maintain their durability while enhancing their texture and color.
Applications of Finishing Surfaces
The finishing surface is applied across multiple industries to enhance both functionality and aesthetics. Here are some key applications:
- Construction and Architecture
In building construction, achieving the right finishing surface is crucial for walls, floors, and ceilings. Options such as polished concrete, stucco, and textured plaster provide durability and style.
- Automotive Industry
The automotive sector relies on advanced finishing surfaces to enhance both aesthetics and protection. Paint coatings, chrome plating, and anti-corrosion treatments are commonly used to improve vehicle durability.
- Woodworking and Furniture
In furniture manufacturing, a well-applied finishing surface ensures durability and enhances the natural beauty of wood. Varnishing, staining, and laminating are popular finishing techniques used for wooden surfaces.
- Metal Fabrication
Metal surfaces require different types of finishes, such as anodizing, powder coating, and electroplating, to prevent rust and improve the metal’s longevity and appearance.
- Electronics and Technology
Electronic devices, including smartphones and laptops, require precision in their finishing surface to ensure durability and a sleek, modern look. Anti-fingerprint coatings and matte or glossy finishes are common in consumer electronics.
- Medical and Pharmaceutical Industry
Medical instruments and equipment require specialized finishing surfaces to maintain hygiene and durability. Stainless steel surgical tools, for example, undergo electropolishing to enhance their corrosion resistance and smoothness.
Benefits of a High-Quality Finishing Surface
A well-executed finishing surface provides numerous advantages across different applications. Some key benefits include:
- Enhanced Durability
Proper finishing helps protect materials from wear, corrosion, and environmental damage, increasing their lifespan.
- Improved Aesthetics
A high-quality finishing surface adds visual appeal, making products more attractive and marketable.
- Better Functionality
Some finishes provide additional benefits, such as water resistance, slip resistance, or UV protection, improving the overall usability of the product.
- Increased Hygiene
In industries like healthcare and food processing, smooth finishing surfaces reduce bacterial buildup, ensuring safety and cleanliness.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs
Materials with a high-quality finishing surface require less maintenance, saving costs in the long run.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Finishing Surface
Selecting the right finishing surface depends on several factors, including:
- Material Type
Different materials require different finishing techniques. For example, metal surfaces may need anodizing or powder coating, while wood may require varnishing or oiling.
- Environmental Conditions
Outdoor surfaces require weather-resistant finishes, while indoor surfaces may focus more on aesthetics.
- Functional Requirements
If the surface will be exposed to heavy use, impact-resistant or scratch-resistant finishes are essential.
- Maintenance Needs
Some finishing surfaces require regular upkeep, while others are designed for low maintenance.
- Cost Considerations
High-end finishes may offer superior performance but can be costly. It’s important to balance quality and budget when selecting a finishing option.
Future Trends in Finishing Surfaces
With advancements in technology, the future of finishing surfaces is evolving. Some notable trends include:
- Smart Coatings: Self-cleaning and antibacterial surfaces that use nanotechnology.
- Eco-Friendly Finishes: Sustainable and non-toxic finishing solutions for environmentally conscious consumers.
- 3D Printed Finishes: Innovations in 3D printing allow for custom textures and designs in finishing surfaces.
Conclusion
The finishing surface is a critical aspect of product design and material durability across various industries. Whether in construction, automotive, metalworking, or consumer electronics, achieving the right finish enhances both functionality and aesthetics. By understanding the different types, applications, and benefits of finishing surfaces, businesses and individuals can make informed decisions to improve the quality and longevity of their materials.
As technology advances, new finishing techniques will continue to emerge, offering even more innovative and sustainable solutions for various industries.