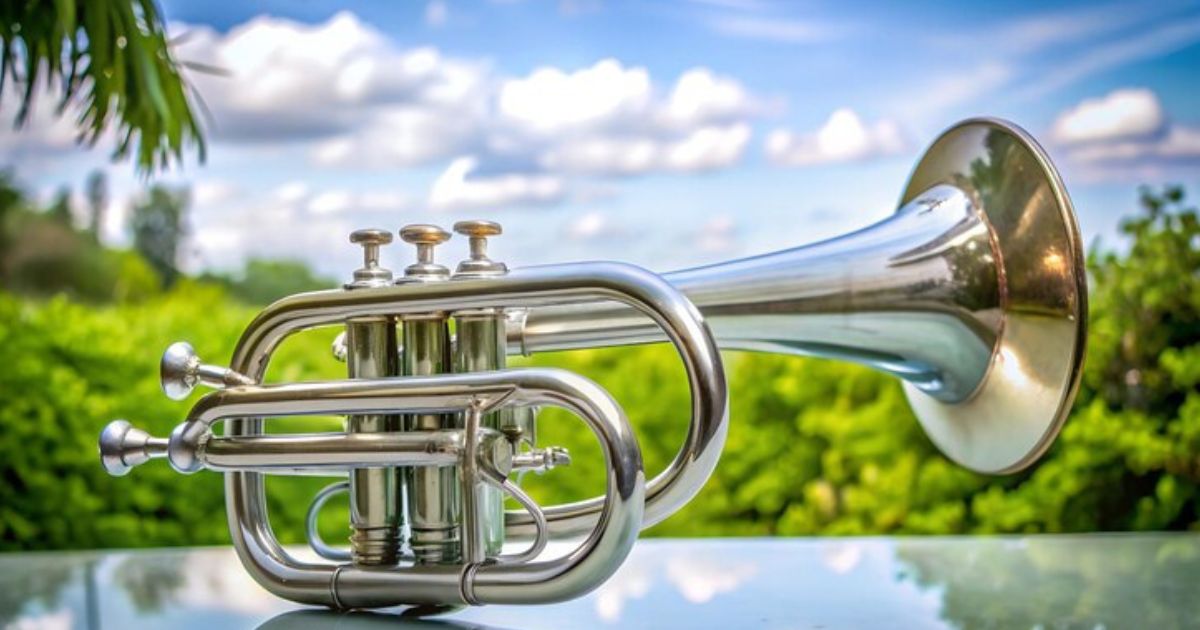
The flugelhorn is a unique and captivating brass instrument that has found its place in jazz bands, brass ensembles, and orchestras. Its mellow tone and versatility make it stand out among other brass instruments. Whether you’re new to music or an experienced musician, understanding the flugelhorn can enhance your appreciation for brass music. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the world of the flugelhorn, exploring its history, features, uses, and much more.
What is a Flugelhorn?
The flugelhorn is a brass wind instrument closely related to the trumpet, but it has a broader, warmer tone. It is often confused with other brass instruments, such as the cornet, due to its similar appearance and sound characteristics. The flugelhorn is typically pitched in B♭, although versions in other keys exist. It is primarily used in jazz, brass bands, and orchestras, known for its rich, mellow sound.
History of the Flugelhorn
The flugelhorn has an interesting history that traces back to the 19th century. It is believed to have originated in the early 1800s in Germany. Initially, it was used in military bands and brass ensembles. Over the years, the instrument’s use has expanded, especially in jazz, where it became a favored instrument of renowned trumpet players who sought a softer and warmer tone.
Flugelhorn vs. Trumpet: Key Differences
One common question people ask is how the flugelhorn differs from the trumpet. While both are brass instruments and share similar characteristics, they differ in several ways. The flugelhorn has a larger, more conical bore, which gives it its characteristic smooth, mellow sound. In contrast, the trumpet has a more cylindrical bore and a brighter, sharper tone. The flugelhorn also has a larger bell, contributing to its distinctive tone.
How the Flugelhorn is Played
The flugelhorn is played similarly to other brass instruments. Players blow air through a mouthpiece, creating a vibration that produces sound. The valves on the instrument are used to change the pitch by altering the length of the tubing. Proper breath control and embouchure (the way a player positions their mouth) are essential for producing the best sound on the flugelhorn.
The Flugelhorn’s Unique Sound
One of the most distinguishing features of the flugelhorn is its sound. Compared to other brass instruments like the trumpet or trombone, the flugelhorn has a much softer and rounder tone. Its sound is often described as mellow, warm, and rich, making it an excellent choice for creating smooth, lyrical lines in music. It has a more relaxed sound, ideal for ballads and jazz solos.
Flugelhorn in Jazz Music
The flugelhorn has found a particular home in jazz music, where its warm tone complements the improvisational nature of the genre. Famous jazz musicians like Art Farmer, Clark Terry, and Chuck Mangione have popularized the flugelhorn, incorporating it into their performances. Its smooth sound allows for expressive phrasing, making it perfect for jazz ballads and melodic solos.
Flugelhorn in Brass Bands
In brass bands, the flugelhorn often plays a similar role to the cornet, providing melodic lines and harmonies. However, its mellow tone gives it a distinctive place in the ensemble. It is usually featured in the brass section along with trumpets and trombones, but its sound blends more seamlessly due to its softer characteristics.
Flugelhorn in Orchestras
Although the flugelhorn is not as commonly used in orchestras as instruments like the trumpet or trombone, it occasionally appears in orchestral compositions. Composers like Gustav Mahler and Leonard Bernstein have written parts for the flugelhorn, recognizing its unique tonal qualities. In orchestral settings, the flugelhorn often plays a more subtle, lyrical role, adding depth and warmth to the brass section.
Types of Flugelhorns
While most flugelhorns are pitched in B♭, there are variations in design and key. Some flugelhorns are designed with a tuning slide that allows for slight adjustments to tuning. Additionally, some flugelhorns feature different mouthpiece designs, which can affect the instrument’s tone and playability. There are also flugelhorns with different bore sizes, which contribute to subtle differences in sound.
Flugelhorn Maintenance Tips
Like any brass instrument, the flugelhorn requires regular maintenance to keep it in top playing condition. This includes cleaning the instrument to prevent buildup of dirt and moisture, oiling the valves to ensure smooth operation, and checking for any dents or damage. Regular maintenance not only improves the sound quality but also extends the lifespan of the instrument.
Choosing the Right Fluge’lhorn
When choosing a flugelhorn, it’s essential to consider factors such as the material, the bore size, and the mouthpiece design. Most flugelhorns are made of brass, but some models may feature gold or silver plating for a slightly different tonal quality. The choice of mouthpiece can also significantly affect the instrument’s sound and playability. Testing the instrument before purchasing is highly recommended.
Flugel’horn in Popular Culture
The flugelhorn has made appearances in popular culture, particularly in jazz and film music. It has been used in soundtracks for movies and TV shows, often to evoke emotions or underscore specific scenes. The flugelh’orn’s distinctive sound makes it an excellent choice for adding atmosphere to a scene, whether it’s a mellow jazz club or a romantic moment in a film.
Flugelho’rn and Its Role in Modern Music
Today, the flug’elhorn continues to play an important role in modern music. It is frequently used in jazz, fusion, and contemporary brass ensembles. Its ability to produce smooth, lyrical melodies makes it an ideal instrument for solo performances, as well as in more complex arrangements where its warmth can shine through. Many modern jazz musicians still prefer the flugelhorn for its unique sound, which is hard to replicate with other brass instruments.
Learning to Play the Flu’gelhorn
If you’re interested in learning to play the flugelhorn, there are a few things to keep in mind. Like other brass instruments, it requires a combination of good technique, practice, and a keen ear for pitch. Beginners may want to start by learning basic brass techniques, including how to hold the instrument and control the airflow. With dedication, even novice musicians can master the flugelhorn and enjoy its beautiful sound.
The Future of the Flugelh’orn
As music continues to evolve, the flugelhorn remains a beloved instrument in jazz, classical, and contemporary music. While it may not be as mainstream as the trumpet or saxophone, it still has a place in the hearts of musicians and listeners alike. Its warm, mellow tone is likely to continue captivating audiences for many years to come.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the fluge’lhorn is a unique and versatile brass instrument with a rich history and a distinctive sound. Whether you’re a jazz enthusiast, a brass musician, or simply someone who enjoys beautiful music, the flug’elhorn is an instrument worth exploring. From its smooth, mellow tone to its contributions in jazz, brass bands, and orchestras, the flugelhorn has proven its value in the world of music.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between a flu’gelhorn and a trumpet? The flugelhorn has a larger, more conical bore and a softer, mellower sound, while the trumpet is brighter and more focused with a cylindrical bore.
Can the flug’elhorn be used in orchestras? Yes, the flugelhorn is occasionally used in orchestral compositions, particularly when a mellow, lyrical tone is needed.
Is the flugel’horn easy to play? Like other brass instruments, learning the flugelhorn requires practice, but with dedication, it is very playable for musicians of all skill levels.
How do I maintain a flugel’horn? Regular cleaning, oiling the valves, and checking for damage are essential to maintain the flugelhorn’s sound and longevity.
What types of music is the flugelh’orn best suited for? The flugelhorn is commonly used in jazz, brass bands, and orchestras, and is particularly favored for its smooth and mellow tone, making it perfect for ballads and melodic solos.