Are you navigating the complex journey of pregnancy and exploring various treatments to ensure a healthy outcome? Many couples face reproductive challenges, making it essential to understand the available options for support. Relevant therapies have gained popularity due to their effectiveness in addressing issues like hormonal imbalances.
For instance, some women experience vaginal swelling in pregnancy, a common concern when using specific treatments. Here, we will explore the effectiveness of vaginal and intramuscular progesterone in supporting pregnancy. By understanding the pros and cons of each process, you will be better equipped to make feasible decisions.
Understanding Progesterone’s Role in Reproduction
This compound plays a crucial role in preparing the uterus for pregnancy, especially in cases of hormonal imbalance. It thickens the uterine lining, creating an optimal environment for the embryo to implant. Its levels must be high early to maintain a healthy process. This hormone can be administered in multiple ways, with vaginal and intramuscular being the most common.
Method of Administration
Vaginal progesterone is administered through suppositories, gels, or tablets directly into the vagina. This allows for convenient and targeted hormone delivery to the uterus. The method is generally easy to use, with minimal systemic side effects due to its direct absorption.
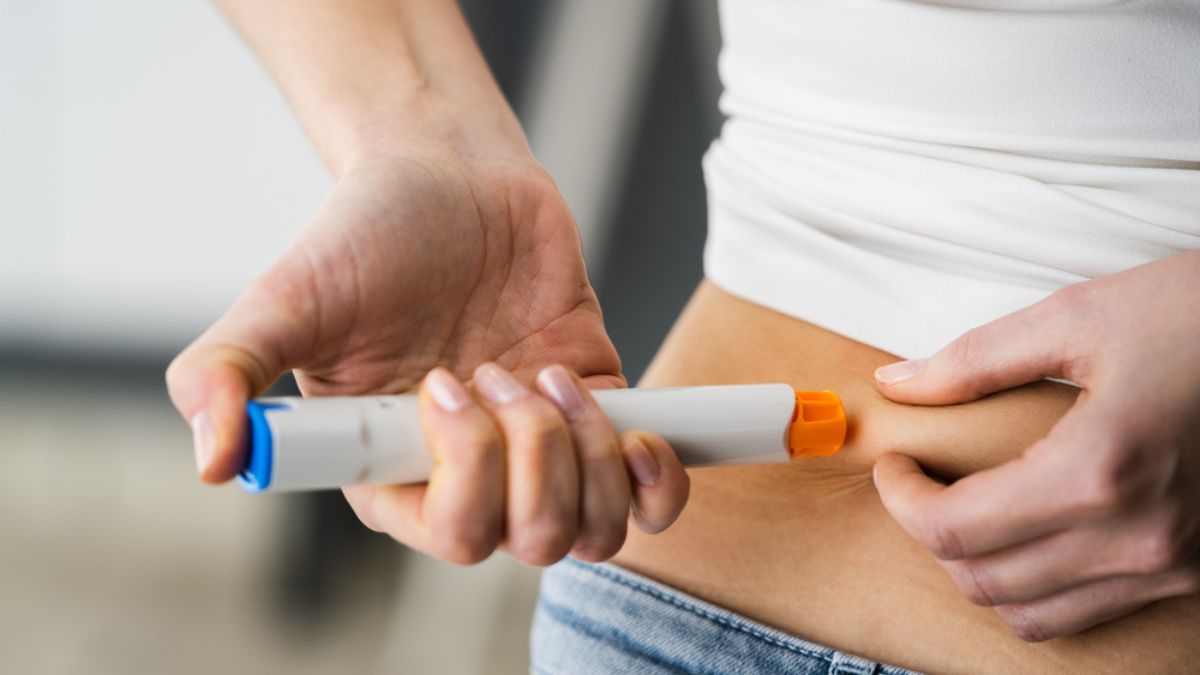
Intramuscular progesterone is administered via injections, typically in the buttocks or thigh muscles. This method requires precise administration by a healthcare professional or self-injection training. Although less convenient, it ensures consistent systemic absorption of this substance throughout the body.
The Effectiveness of These Methods
Vaginal progesterone is effective for women with recurrent miscarriages or undergoing assisted reproductive technology (ART). This procedure’s localized action ensures the hormone reaches the uterus directly, aiding embryo implantation. Lower doses suffice as direct delivery to the uterus reduces the risk of side effects.
Intramuscular progesterone’s systemic absorption ensures adequate levels are maintained throughout the body. It is recommended for women with luteal phase defects or those unresponsive to vaginal progesterone treatment. The consistent delivery of this substance via intramuscular injections provides a reliable option for maintaining hormone levels.
The Dosage Requirements
Vaginal progesterone generally requires lower doses due to its direct delivery to the uterus. The application allows for adequate hormone levels with minimal systemic exposure. This method reduces the risk of side effects while maintaining the necessary hormones for pregnancy support.
Intramuscular progesterone typically involves higher doses to achieve adequate systemic hormone levels throughout the body. The injections ensure consistent absorption, supporting pregnancies at higher risk of complications. Despite higher doses, this method is effective for those needing comprehensive supplementation.
The Process of Absorption
Vaginal progesterone delivers the compound directly to the uterus, ensuring efficient absorption. Such delivery minimizes systemic circulation, making lower doses effective in female Infertility support. The hormone is absorbed primarily through the vaginal lining, directly impacting the uterine environment.
Intramuscular progesterone involves injecting the hormone into the muscle, leading to systemic absorption into the bloodstream. This method ensures consistent and widespread hormone levels, supporting the body’s needs. The systemic circulation allows for reliable hormone distribution, making it effective in maintaining pregnancy.
Side Effects and Considerations
Vaginal swelling is one of the most common concerns during this whole process. This swelling can cause discomfort and may lead to other issues, such as irritation or infection. However, many women find that the benefits of vaginal progesterone outweigh the potential drawbacks. Proper hygiene and using remedies can help manage these side effects effectively.
While effective, the intramuscular process can also have side effects. The most common issues include pain at the injection site, soreness, and sometimes bruising. These side effects can be bothersome, especially if injections are required daily. Despite the discomfort, many women and healthcare providers choose this process for its reliable effectiveness in high-risk pregnancies.
So, if you are experiencing vaginal swelling in pregnancy, it is important to discuss with your doctor promptly. Discussing the above-mentioned options with your healthcare provider ensures the most suitable progesterone method. Expert guidance is vital in ensuring a healthy and smooth pregnancy experience.