In our quest for the elixir of life, science has brought forward a molecule that has taken center stage in the discussion of aging and longevity: Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide, commonly known as NAD. This vital coenzyme found in all living cells has shown promising effects on the aging process, playing a significant role in the metabolic functions that keep us healthy and energetic. As the interest in anti-aging research burgeons, understanding how NAD influences cellular health could unlock novel approaches to enhance our lifespan and well-being. Below, we delve into the fascinating world of NAD and its potential implications for age management strategies.
Exploring the Role of NAD in Cellular Health and Longevity
NAD is a vital coenzyme involved in essential biological processes like energy metabolism, DNA repair, and gene expression. It plays a key role in converting nutrients into energy, but levels of NAD naturally decline with age, leading to compromised cellular function and health issues. Studies suggest that maintaining healthy NAD levels can support cellular operations and help preserve genomic stability.
Research highlights the link between NAD and sirtuins, proteins that promote longevity and reduce oxidative stress. Since sirtuins rely on NAD to function, boosting NAD levels could help protect against cellular aging. This makes NAD a promising target for longevity studies. Learn more about its benefits at www.nad.com.
The Science Behind NAD and Its Impact on the Aging Process
NAD is crucial for mitochondrial function, promoting energy homeostasis and reducing metabolic stress’s effects on aging. It also plays a role in preventing age-related diseases by activating pathways that repair damaged DNA, which is linked to preventing malignancy and neurodegeneration.
The relationship between NAD and longevity extends to telomere integrity, which can trigger cellular senescence when eroded. NAD has been associated with telomerase activity, potentially preventing premature cellular aging. Despite these advances, the scientific investigation into NAD and aging is continually evolving. Evidence suggests that optimal NAD levels may attenuate aging and provide a buffer against biological stressors.
Boosting NAD Levels Naturally for Enhanced Vitality
Regular exercise can increase cellular NAD levels, potentially delaying the aging process through improved metabolic function and resilience. Dietary patterns, including those found in milk, fish, and mushrooms, can also boost NAD availability, supporting cellular processes that combat age-related decline.
Caloric restriction (CR) has been consistently associated with an increase in life span across several species, partly due to higher NAD levels promoted by CR. These natural means of augmenting NAD availability complement emerging therapeutics and suggest that with mindful lifestyle choices, we can nudge our biology in favor of a more graceful aging process. These interventions offer a preventative health approach and complement emerging therapeutics.
NAD Products and Anti-aging: Evaluating the Evidence
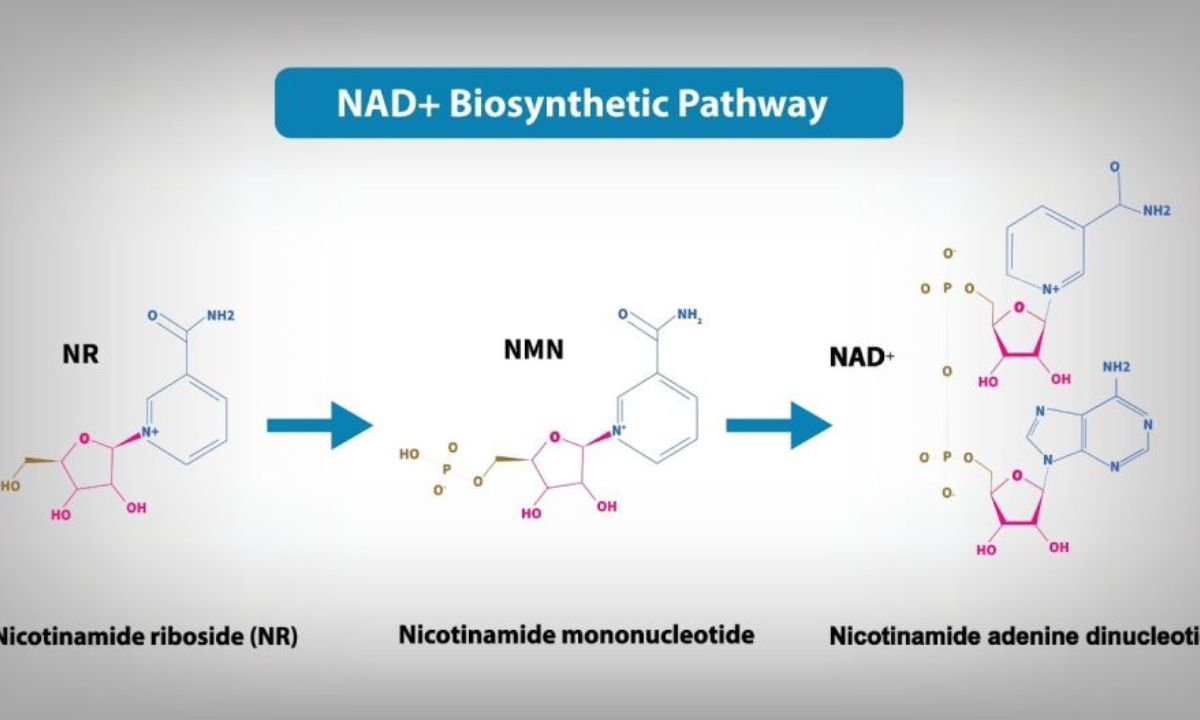
The market for NAD products has grown due to increasing interest, offering potential benefits such as enhanced energy, mental clarity, and anti-aging effects. Precursors to NAD, such as nicotinamide riboside and nicotinamide mononucleotide, have gained popularity for their potential to boost NAD levels.
However, human trials are ongoing to evaluate their long-term impact, and critics argue for more comprehensive studies to support these claims. Initial studies show that NAD products can increase blood cell NAD concentrations, but translating these changes into clinically meaningful outcomes like delayed aging or improved healthspan is still a research area. NAD nutraceuticals offers hope for those seeking to mitigate aging effects, but it also emphasizes the need for rigorous scientific validation.
Future Directions in NAD Research and Its Potential in Age Management Strategies
NAD research holds great potential as scientists explore its impact on aging and develop therapeutics to boost NAD levels. Trials are underway to address specific age-related conditions, with potential applications in treating diseases primarily affecting the elderly. Gene therapies, targeted nutrition, and synthetic biology are promising in NAD and age management, contributing to longevity science. However, the ethical and societal implications of anti-aging interventions will shape research in NAD and longevity.
Conversation and regulation must evolve alongside scientific progress to ensure equitable and responsible access to potential benefits. Current investigations focus on understanding the underpinnings of aging and how molecular interventions could extend healthy years of life, with NAD at the forefront of this scientific pursuit.
Overall, the nexus between NAD and aging presents an intriguing landscape of possibilities for enhancing healthspan. As research continues to evolve, it beckons a future where aging is not so much about adding years to life, but more significantly, adding life to years.
ALSO READ: How Orthodontic Treatment Can Improve Your Overall Appearance






![Laydson Group Review: Importance of a Unique and Clear Business Function [laydson.com]](https://hackerella.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/unnamed-87-150x150.jpg)